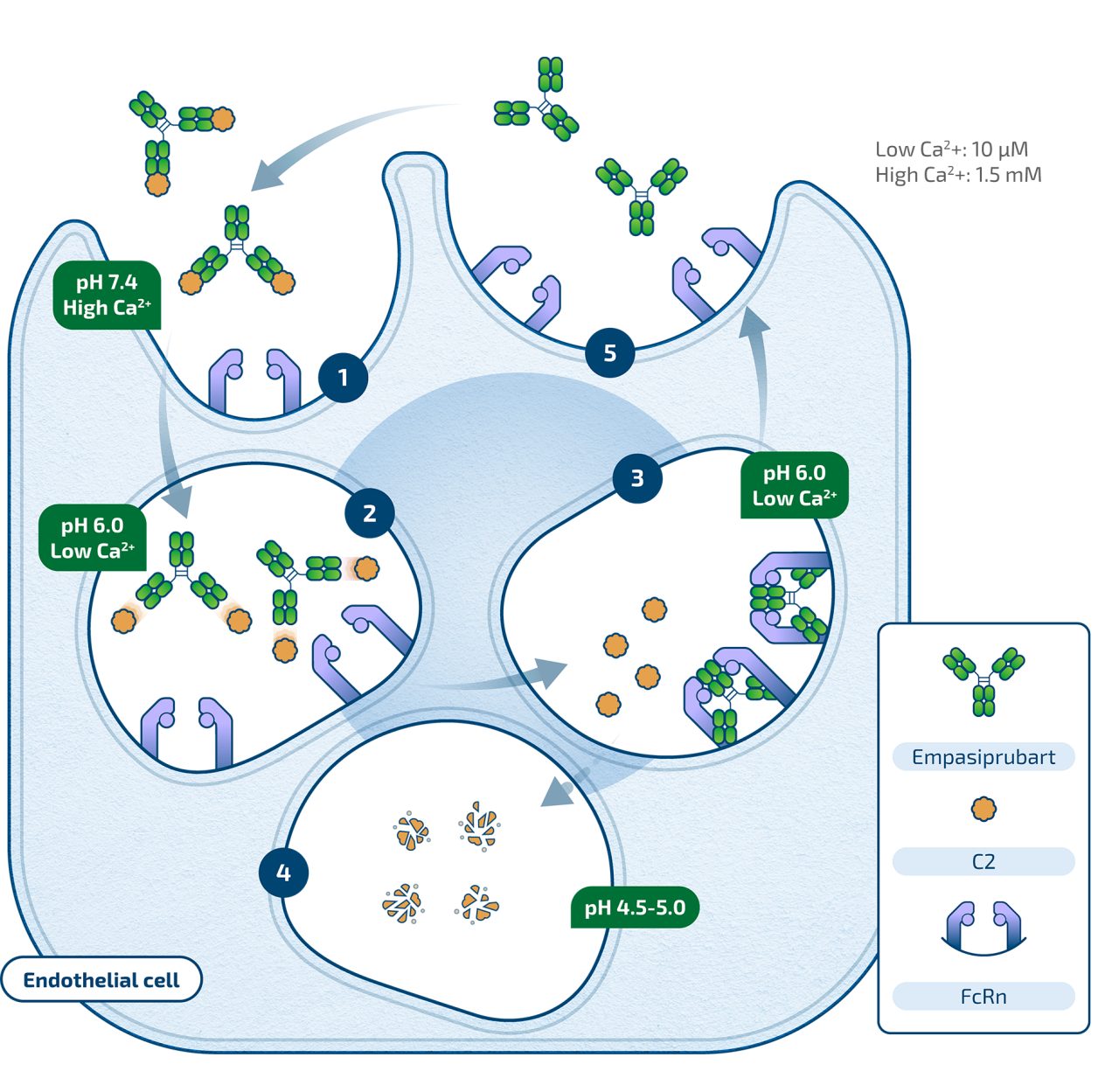
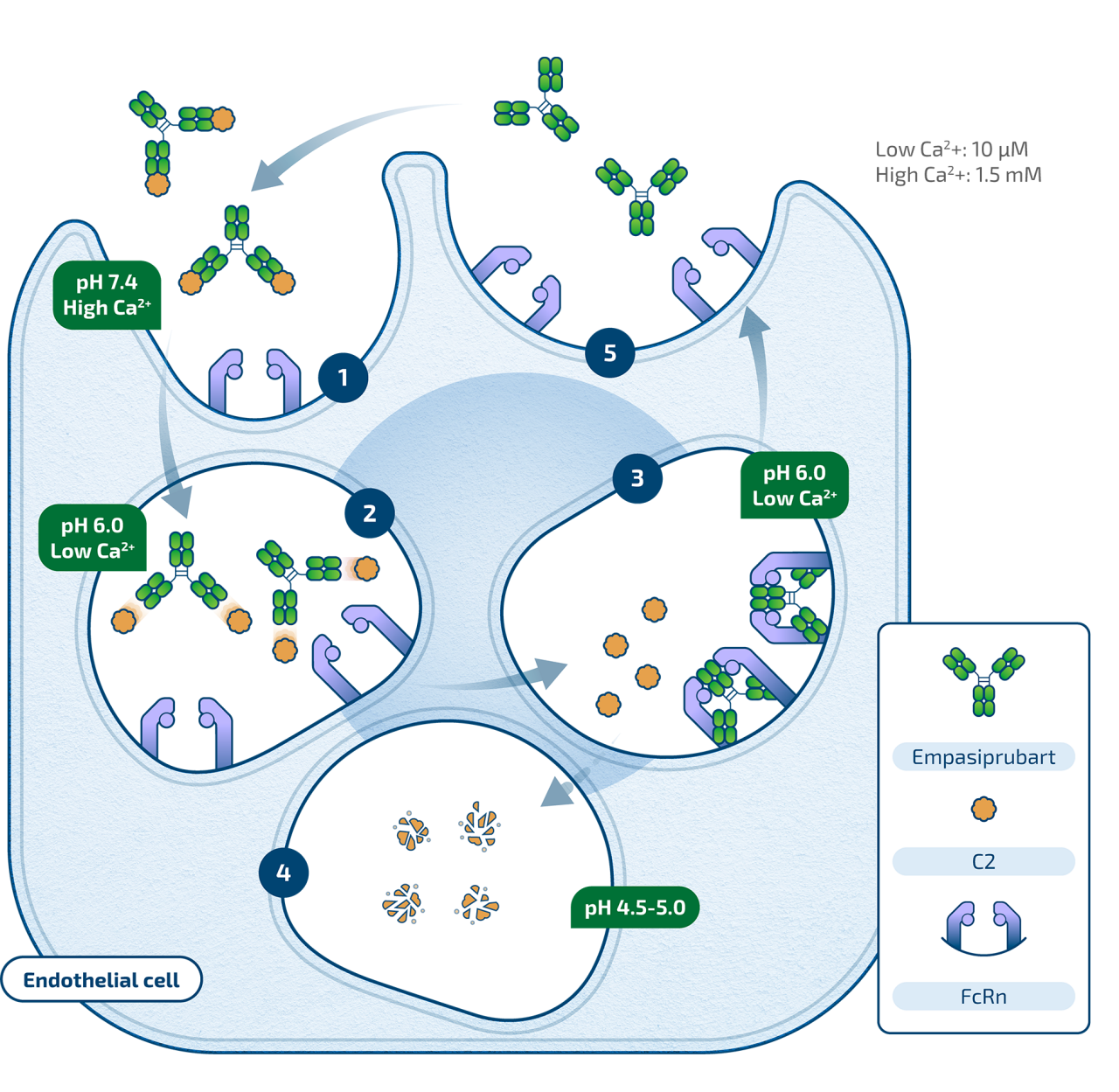
Empasiprubart (formerly ARGX-117) is designed to be a humanized sweeping antibody that binds specifically to C2 in a pH- and Ca2+- dependent manner. C2 is a protein in the complement cascade which, when activated, leads to cell destruction. Binding of Empasiprubart is intended to inhibit the function of C2 and downstream complement activation.
By blocking complement activity, Empasiprubart has the potential to reduce tissue inflammation and the adaptive immune response. Through this proposed mechanism, Empasiprubart could represent a broad pipeline opportunity across severe autoimmune indications.