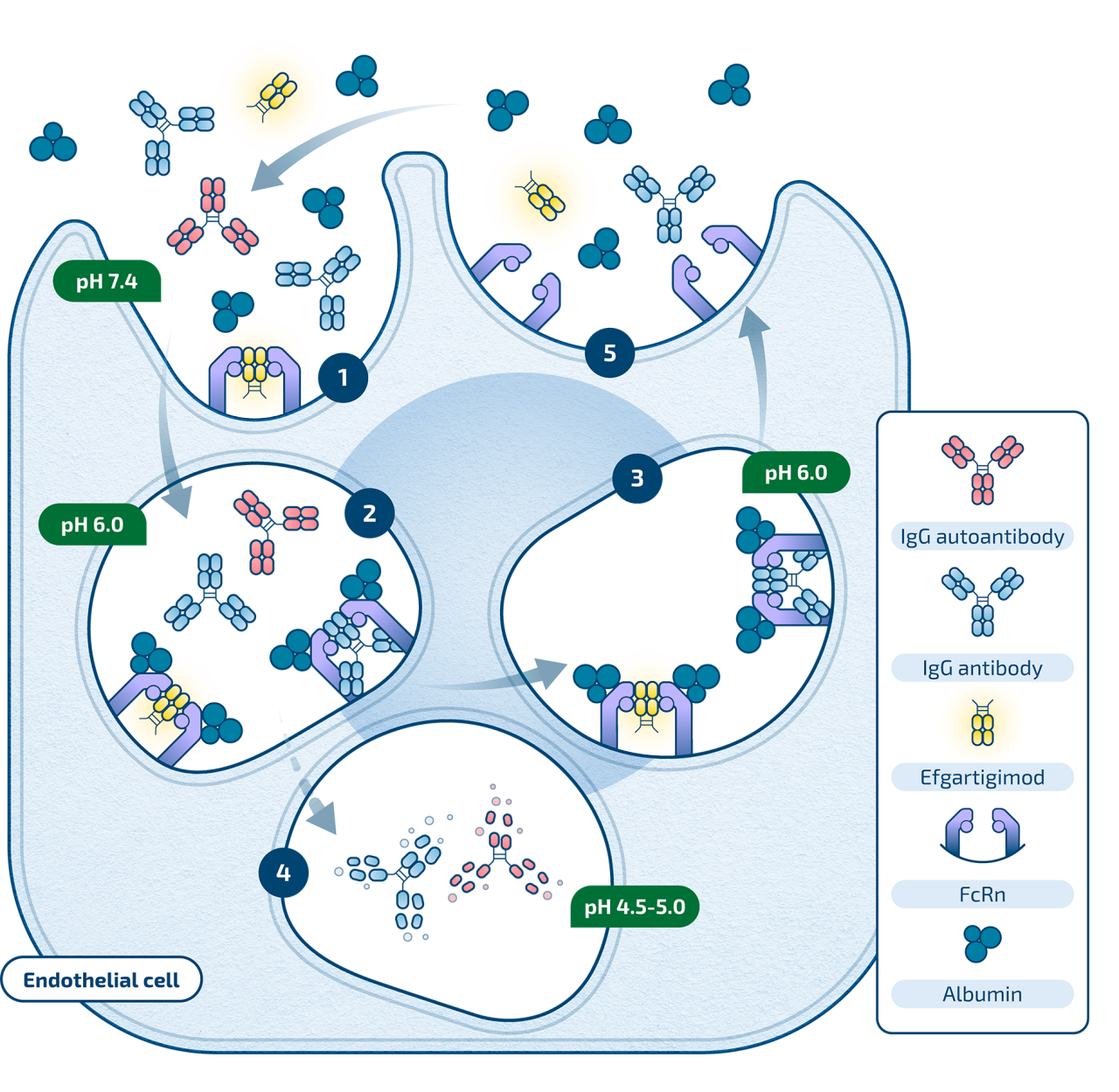
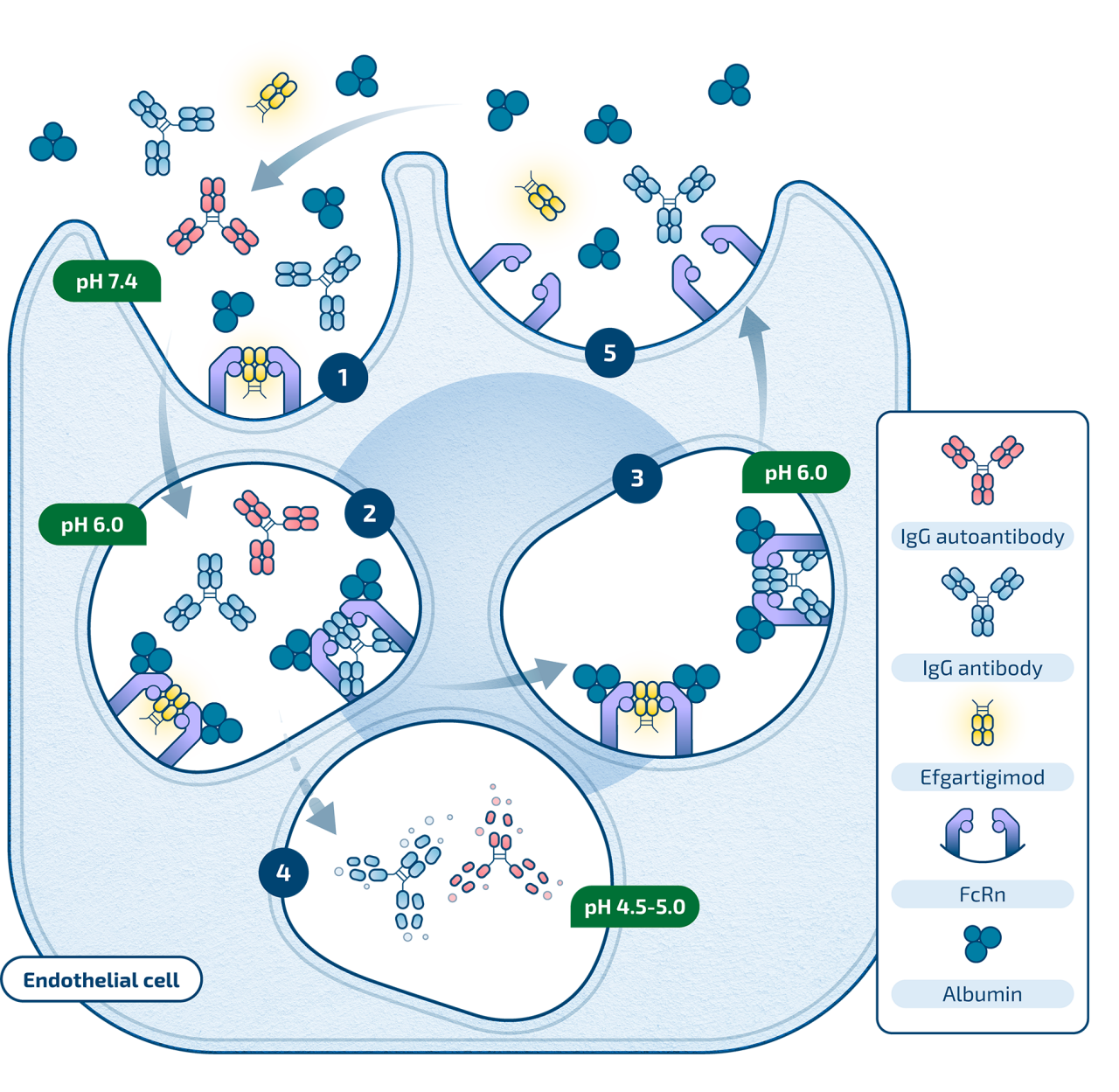
(1) Efgartigimod and IgG are internalized into the cell
(2) Efgartigimod outcompetes endogenous IgG antibodies and pathogenic IgG autoantibodies for binding to FcRn, due to increased affinity to FcRn
(3) When bound to FcRn, efgartigimod and IgG escape lysosomal degradation
(4) Remaining unbound IgG and efgartigimod are degraded in the lysosome
(5) Efgartigimod and fewer IgGs are recycled back into circulation